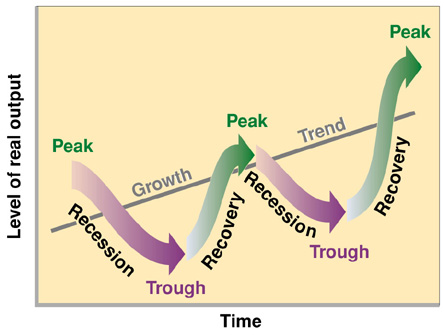
bottom
recovery
peak or top
recession.
BOTTOM OF THE BUSINESS CYCLE
At the bottom of the business cycle:
unemployment rate is high so that fewer people buy housing.
prices are low including the price of raw material.
both consumers and businesses act conservatively, being reluctant to commit themselves to long term borrowing or investment.
government policies are expansionary. for example, "real" interest rates are low and taxes are geared to encourage investment and employment. Those industries that do expand do so at a low cost after tax.
RECOVERY IN THE BUSINESS CYCLE
as more and more consumers and businesses sense an improvement in the economy they start to invest and buy more.
consumers buy more houses and expensive items such as prestige cars.
low interest rates allow affordable finance for both housing , goods and services.
as the economy expands businesses borrow more.
PEAK OF THE BUSINESS CYCLE
the price of goods rise in response to increased demand and increased costs
real estate activity reaches a high point and consumers become anxious to buy now "to beat rising prices".
fixed interest investments lose ground to more flexible investments such as property trusts.
the government expands social programs including public housing.
deficit spending continues and inflation raises. The government becomes concerned about rising inflation and the deficit, so that fiscal and monetary policies are implemented to dampen demand. That is, an increase in interest rates and a general tightening of money supply.
the first to feel the fiscal tightening is the consumer, credit unions, and banks as depositors remove their money to deposit into higher paying investments.
a number of firms and consumers are forced to sell assets to remain liquid.
real estate and construction activity moderates, workers are laid off as construction projects are aborted but some projects which began earlier, will continue to completion.
RECESSION IN THE BUSINESS CYCLE
The recessionary phase is illustrated by:
high interest rates cause escalating costs which manufacturers try to pass onto the consumer.
inflation becomes the nation's "number one enemy" and the government tightens the money supply even further.
workers are laid off as companies can no longer afford the high interest rates, unemployment increases and demand for goods and services gradually decreases.
pressure is put on the government to ease monetary policy, it reluctantly agrees by reducing interest rates but the real rate (nominal rate less inflation) is still high.
business curtails development and expansion.
consumers stay out of the market place.
The cycle shows how important r1scal and monetary policy is in the real estate market and this sensitivity is utilized by governments to indirectly control the economy. Real estate gets the residual money available after governments and business. This accentuates the real estate cycle which is more exaggerated than the business cycle. Investment in real estate is subject to the following disadvantages compared to the more flexible and liquid investments such as shares:
ILLIQUID: Real estate by its nature cannot be quickly converted into cash. The long lead time increases the risk of investment and therefore, the investor requires a higher rate of return as compensation.
IMPERFECT KNOWLEDGE: The real estate investor does not readily know the value of a real estate investment at any one time. However, it should be recognised that there is no such thing as a "perfect" market in any investment field. The oft quoted share market as an example of a high level of knowledge (because of daily quoted company share prices) is exaggerated as the sharemarket investor has an intangible right in a company and few stock market investors understand at the higher level, the complexities of company law and published financial statements of companies.
On the other hand, the tangible nature of real estate, the role of the agent as middle man and a number of other reasons effectively raises the knowledge of real estate investors to a higher level than that admitted by most valuation and economic commentators.
